Model Exchange Protocol
The Model Exchange Protocol enables your application to securely request and receive configured language models from FlowDown. Instead of asking users to copy-paste sensitive credentials, you can use the FlowDownModelExchange framework to handle the secure handshake and data transfer.
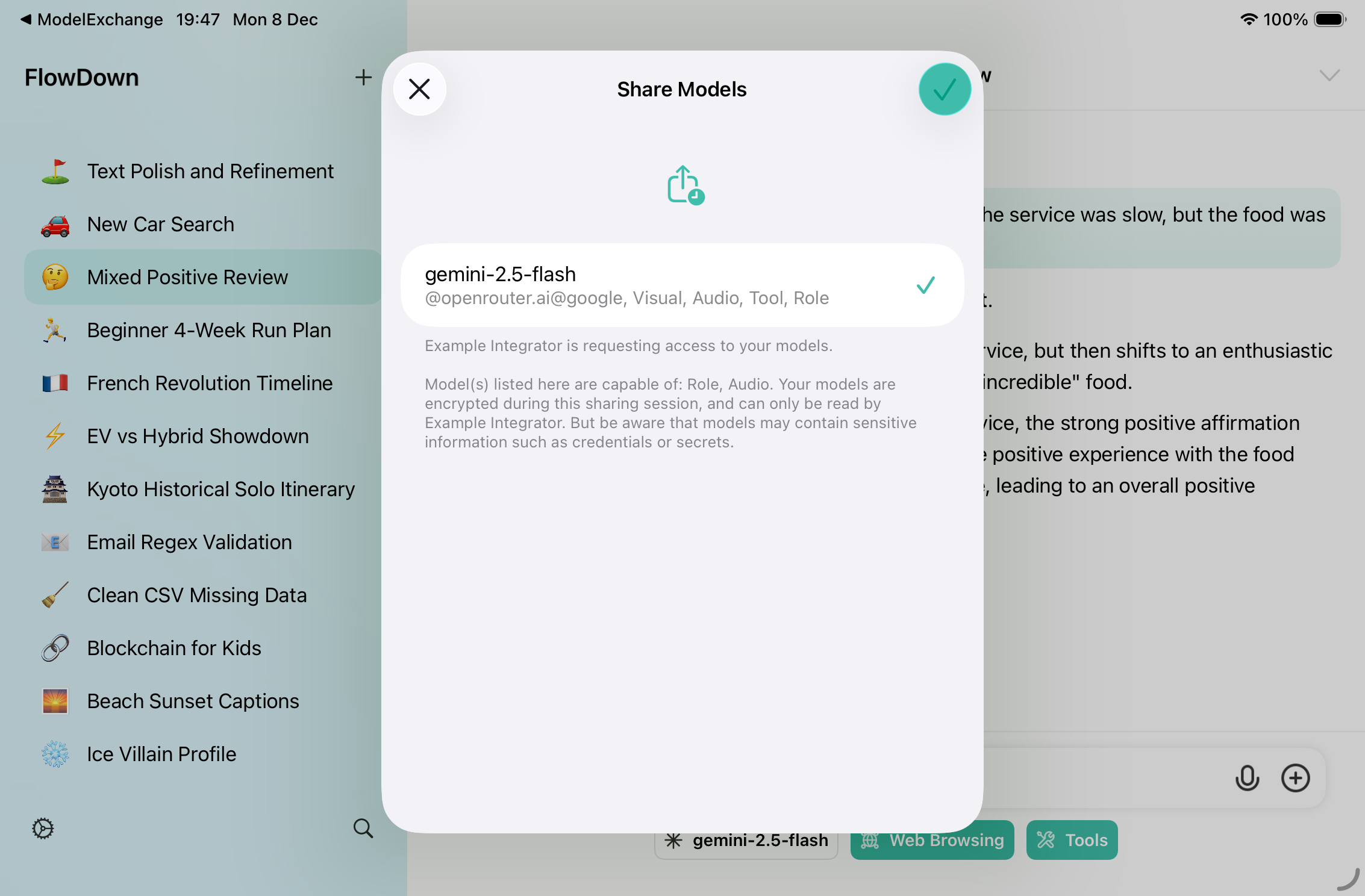
::: info Version Requirement This protocol requires FlowDown version 4.1.4 or later installed on the user's device. :::
Installation
Currently, FlowDownModelExchange is distributed as part of the FlowDown source tree and not hosted on a separate public repository. You need to integrate it manually.
- Locate the directory
Frameworks/FlowDownModelExchangein the FlowDown repository. - Copy the entire folder into your project workspace.
- Add it as a Local Package in Xcode (File -> Add Package Dependencies -> Add Local...), or directly include the source files in your target.
Usage
1. Initialization
First, initialize a key pair. You should persist this key pair if you want to maintain the same identity across sessions, or generate a new one for each session.
import FlowDownModelExchange
// Generate a new key pair for encryption and signing
let keyPair = ModelExchangeKeyPair()
// Initialize the request builder
let builder = ModelExchangeRequestBuilder(
callbackScheme: "my-app-scheme", // Your app's URL scheme
keyPair: keyPair
)
2. Request Models
When you want to request models from FlowDown, use the builder to create a signed URL and open it.
func requestModels() {
do {
// Create a signed request URL
let request = try builder.makeExchangeURL(
session: UUID().uuidString,
appName: "My Awesome App",
reason: "To assist with coding tasks",
capabilities: [.audio, .developerRole], // Filter needed models
multipleSelection: false
)
// Open FlowDown
UIApplication.shared.open(request.url)
} catch {
print("Failed to build request: \(error)")
}
}
3. Handle Response
Configure your app to handle the callback URL (e.g., in onOpenURL or AppDelegate).
func handleCallback(url: URL) {
guard let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: false),
let queryItems = components.queryItems else { return }
let params = Dictionary(uniqueKeysWithValues: queryItems.map { ($0.name, $0.value ?? "") })
// Check the stage
if params["stage"] == "completed" {
handleCompletion(params: params)
} else if params["stage"] == "cancelled" {
print("User cancelled the operation")
}
}
4. Decrypt Payload
Once you receive the completed callback, use the framework to decode and decrypt the payload.
func handleCompletion(params: [String: String]) {
guard let payloadString = params["payload"],
let sessionID = params["session"] else { return }
do {
// 1. Decode the encrypted payload wrapper
let encryptedPayload = try ModelExchangeEncryptedPayload.decode(from: payloadString)
// 2. Decrypt the data using your key pair
let decryptedData = try ModelExchangeCrypto.decrypt(
encryptedPayload,
with: keyPair
)
// 3. Parse the model data (usually a Property List)
let models = try PropertyListSerialization.propertyList(
from: decryptedData,
options: [],
format: nil
)
print("Received models: \(models)")
} catch {
print("Decryption failed: \(error)")
}
}
Security
The framework handles the security details for you:
- Signatures: Requests are signed with your private key to prevent tampering.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted using
ChaChaPoly(Symmetric) andCurve25519(Key Agreement). - Forward Secrecy: Ephemeral keys are used for the exchange session.
Data Format
The decrypted data is a serialized Property List (Plist) containing:
- Model display names
- Endpoint URLs
- Authentication headers (including sensitive credentials)
- Model capabilities
Treat this data with the highest level of security. Do not log sensitive fields in production.